ebm¶
digraph inheritancecf2c842c9d { bgcolor=transparent; rankdir=LR; ratio=expand; size=""; "EBM" [URL="#climlab.model.ebm.EBM",dirType=back,fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=14,height=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="A parent class for all Energy-Balance-Model classes."]; "TimeDependentProcess" -> "EBM" [arrowsize=0.5,dirType=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "EBM_annual" [URL="#climlab.model.ebm.EBM_annual",dirType=back,fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=14,height=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top"]; "EBM_seasonal" -> "EBM_annual" [arrowsize=0.5,dirType=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "EBM_seasonal" [URL="#climlab.model.ebm.EBM_seasonal",dirType=back,fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=14,height=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top"]; "EBM" -> "EBM_seasonal" [arrowsize=0.5,dirType=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; "Process" [URL="climlab.process.process.html#climlab.process.process.Process",dirType=back,fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=14,height=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="A generic parent class for all climlab process objects."]; "TimeDependentProcess" [URL="climlab.process.time_dependent_process.html#climlab.process.time_dependent_process.TimeDependentProcess",dirType=back,fillcolor=white,fontname="Vera Sans, DejaVu Sans, Liberation Sans, Arial, Helvetica, sans",fontsize=14,height=0.25,shape=box,style="setlinewidth(0.5),filled",target="_top",tooltip="A generic parent class for all time-dependent processes."]; "Process" -> "TimeDependentProcess" [arrowsize=0.5,dirType=back,style="setlinewidth(0.5)"]; }Convenience classes for pre-made Energy Balance Models in CLIMLAB.
These models all solve some form of the equation
where
\(\phi\) is latitude
\(T_s\) is a zonally averaged surface temperature
\(C\) is a depth-integrated heat capacity
\(\alpha\) is an albedo (which may depend on latitude and/or temperature)
\(S(\phi, t)\) is the insolation
\(\left[A + B T_s \right]\) is a parameterization of the Outgoing Longwave Radiation to space
the last term on the right hand side is a diffusive heat transport convergence with thermal diffusivity \(D\) in the same units as \(B\)
Three classes are provided, which differ in the type of insolation \(S\):
climlab.EBMuses a steady idealized annual insolation (second Legendre polynomial form)climlab.EBM_annualuses realistic steady annual-mean insolationclimlab.EBM_seasonaluses realistic seasonally varying insolation
The __init__ method of class EBM shows how these models are assembled
from subprocesses representing each term in the above equation.
Building the Moist EBM¶
There is currently no ready-made convenience class for the moist EBM,
but it can be readily built by swapping out the dry heat diffusion process climlab.dynamics.MeridionalHeatDiffusion
with the moist equivalent climlab.dynamics.MeridionalMoistDiffusion.
This sort of mixing and matching of model components is at the heart of CLIMLAB design and functionality.
- Example:
We can run both models out to equilibrium and compare the results as follows:
- Example:
- class climlab.model.ebm.EBM(num_lat=90, num_lon=None, S0=1365.2, s2=-0.48, A=210.0, B=2.0, D=0.555, water_depth=10.0, Tf=-10.0, a0=0.3, a2=0.078, ai=0.62, timestep=350632.51200000005, T0=12.0, T2=-40.0, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
TimeDependentProcessA parent class for all Energy-Balance-Model classes.
This class sets up a typical EnergyBalance Model with following subprocesses:
Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR) parametrization through
AplusBTAbsorbed Shortwave Radiation (ASR) through
SimpleAbsorbedShortwavesolar insolation paramtrization through
P2Insolationalbedo parametrization in dependence of temperature through
StepFunctionAlbedoenergy diffusion through
MeridionalHeatDiffusion
Initialization parameters
An instance of
EBMis initialized with the following arguments (for detailed information see Object attributes below):- Parameters:
num_lat (int) –
number of equally spaced points for the latitue grid. Used for domain intialization of
zonal_mean_surfacedefault value:
90
num_lon (int) –
number of equally spaced points in longitude
default value:
None
S0 (float) –
solar constant
unit: \(\frac{\textrm{W}}{\textrm{m}^2}\)
default value:
1365.2
A (float) –
parameter for linear OLR parametrization
AplusBTunit: \(\frac{\textrm{W}}{\textrm{m}^2}\)
default value:
210.0
B (float) –
parameter for linear OLR parametrization
AplusBTunit: \(\frac{\textrm{W}}{\textrm{m}^2 \ ^{\circ} \textrm{C}}\)
default value:
2.0
D (float) –
diffusion parameter for Meridional Energy Diffusion
MeridionalDiffusionunit: \(\frac{\textrm{W}}{\textrm{m}^2 \ ^{\circ} \textrm{C}}\)
default value:
0.555
water_depth (float) –
depth of
zonal_mean_surfacedomain, which the heat capacity is dependent onunit: meters
default value:
10.0
Tf (float) –
freezing temperature
unit: \(^{\circ} \textrm{C}\)
default value:
-10.0
a0 (float) –
base value for planetary albedo parametrization
StepFunctionAlbedounit: dimensionless
default value:
0.3
a2 (float) –
parabolic value for planetary albedo parametrization
StepFunctionAlbedounit: dimensionless
default value:
0.078
ai (float) –
value for ice albedo paramerization in
StepFunctionAlbedounit: dimensionless
default value:
0.62
timestep (float) –
specifies the EBM’s timestep
unit: seconds
default value: (365.2422 * 24 * 60 * 60 ) / 90
-> (90 timesteps per year)
T0 (float) –
base value for initial temperature
unit \(^{\circ} \textrm{C}\)
default value:
12
T2 (float) –
factor for 2nd Legendre polynomial
P2to calculate initial temperatureunit: dimensionless
default value:
40
Object attributes
Additional to the parent class
EnergyBudgetfollowing object attributes are generated and updated during initialization:- Variables:
param (dict) – The parameter dictionary is updated with a couple of the initatilzation input arguments, namely
'S0','A','B','D','Tf','water_depth','a0','a2'and'ai'.domains (dict) – If the object’s
domainsand thestatedictionaries are empty during initialization a domainsfcis created throughzonal_mean_surface(). In the meantime the object’sdomainsandstatedictionaries are updated.subprocess (dict) – Several subprocesses are created (see above) through calling
add_subprocess()and therefore the subprocess dictionary is updated.topdown (bool) – is set to
Falseto call subprocess compute methods first. See alsoTimeDependentProcess.diagnostics (dict) – is initialized with keys:
'OLR','ASR','net_radiation','albedo','icelat'and'ice_area'throughadd_diagnostic().
- Example:
Creation and integration of the preconfigured Energy Balance Model:
>>> import climlab >>> model = climlab.EBM() >>> model.integrate_years(2.) Integrating for 180 steps, 730.4844 days, or 2.0 years. Total elapsed time is 2.0 years.
For more information how to use the EBM class, see the Tutorials chapter.
- Attributes:
- S0
depthDepth at grid centers (m)
depth_boundsDepth at grid interfaces (m)
diagnosticsDictionary access to all diagnostic variables
inputDictionary access to all input variables
latLatitude of grid centers (degrees North)
lat_boundsLatitude of grid interfaces (degrees North)
levPressure levels at grid centers (hPa or mb)
lev_boundsPressure levels at grid interfaces (hPa or mb)
lonLongitude of grid centers (degrees)
lon_boundsLongitude of grid interfaces (degrees)
timestepThe amount of time over which
step_forward()is integrating in unit seconds.
Methods
add_diagnostic(name[, value])Create a new diagnostic variable called
namefor this process and initialize it with the givenvalue.add_input(name[, value])Create a new input variable called
namefor this process and initialize it with the givenvalue.add_subprocess(name, proc)Adds a single subprocess to this process.
add_subprocesses(procdict)Adds a dictionary of subproceses to this process.
compute()Computes the tendencies for all state variables given current state and specified input.
compute_diagnostics([num_iter])Compute all tendencies and diagnostics, but don't update model state.
declare_diagnostics(diaglist)Add the variable names in
inputlistto the list of diagnostics.declare_input(inputlist)Add the variable names in
inputlistto the list of necessary inputs.Compute instantaneous diffusive heat transport in unit \(\textrm{PW}\) on the staggered grid (bounds) through calculating:
Convenience method to compute global mean surface temperature.
Calculates the inferred heat transport by integrating the TOA energy imbalance from pole to pole.
integrate_converge([crit, verbose])Integrates the model until model states are converging.
integrate_days([days, verbose])Integrates the model forward for a specified number of days.
integrate_years([years, verbose])Integrates the model by a given number of years.
remove_diagnostic(name)Removes a diagnostic from the
process.diagnosticdictionary and also delete the associated process attribute.remove_subprocess(name[, verbose])Removes a single subprocess from this process.
set_state(name, value)Sets the variable
nameto a new statevalue.set_timestep([timestep, num_steps_per_year])Calculates the timestep in unit seconds and calls the setter function of
timestep()step_forward()Updates state variables with computed tendencies.
to_xarray([diagnostics])Convert process variables to
xarray.Datasetformat.- property S0¶
- diffusive_heat_transport()[source]¶
Compute instantaneous diffusive heat transport in unit \(\textrm{PW}\) on the staggered grid (bounds) through calculating:
\[H(\varphi) = - 2 \pi R^2 cos(\varphi) D \frac{dT}{d\varphi} \approx - 2 \pi R^2 cos(\varphi) D \frac{\Delta T}{\Delta \varphi}\]- Return type:
array of size
np.size(self.lat_bounds)
THIS IS DEPRECATED AND WILL BE REMOVED IN THE FUTURE. Use the diagnostic
heat_transportinstead, which implements the same calculation.
- global_mean_temperature()[source]¶
Convenience method to compute global mean surface temperature.
Calls
global_mean()method which for the object attriuteTswhich calculates the latitude weighted global mean of a field.- Example:
Calculating the global mean temperature of initial EBM temperature:
>>> import climlab >>> model = climlab.EBM(T0=14., T2=-25) >>> model.global_mean_temperature() Field(13.99873037400856)
- inferred_heat_transport()[source]¶
Calculates the inferred heat transport by integrating the TOA energy imbalance from pole to pole.
The method is calculating
\[H(\varphi) = 2 \pi R^2 \int_{-\pi/2}^{\varphi} cos\phi \ R_{TOA} d\phi\]where \(R_{TOA}\) is the net radiation at top of atmosphere.
- Returns:
total heat transport on the latitude grid in unit \(\textrm{PW}\)
- Return type:
array of size
np.size(self.lat_lat)- Example:
import climlab import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # creating & integrating model model = climlab.EBM() model.step_forward() # plot fig = plt.figure( figsize=(6,4)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.plot(model.lat, model.inferred_heat_transport()) ax.set_title('inferred heat transport') ax.set_xlabel('latitude') ax.set_xticks([-90,-60,-30,0,30,60,90]) ax.set_ylabel('energy (PW)') plt.axhline(linewidth=2, color='grey', linestyle='dashed') plt.show()
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)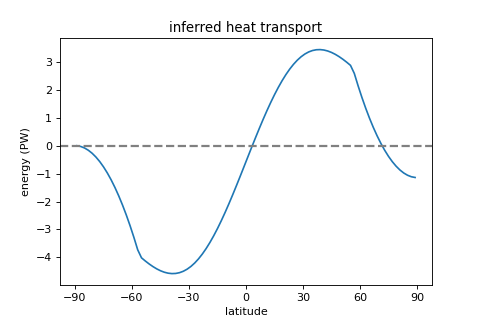
- class climlab.model.ebm.EBM_annual(**kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
EBM_seasonalA class that implements Energy Balance Models with annual mean insolation.
The annual solar distribution is calculated through averaging the
DailyInsolationover time which has been used in used in the parent classEBM_seasonal. That is done by the subprocessAnnualMeanInsolationwhich is more realistic than theP2Insolationmodule used in the classicalEBMclass.According to the parent class
EBM_seasonalthe model will not have an ice-albedo feedback, if albedo ice parameter'ai'is not given. For details see there.Object attributes
Following object attributes are updated during initialization:
- Variables:
subprocess (dict) – suprocess
'insolation'is overwritten byAnnualMeanInsolation- Example:
The
EBM_annualclass uses a different insolation subprocess than theEBMclass:>>> import climlab >>> model_annual = climlab.EBM_annual() >>> print model_annual
climlab Process of type <class 'climlab.model.ebm.EBM_annual'>. State variables and domain shapes: Ts: (90, 1) The subprocess tree: top: <class 'climlab.EBM_annual'> diffusion: <class 'climlab.dynamics.MeridionalHeatDiffusion'> LW: <class 'climlab.radiation.AplusBT'> albedo: <class 'climlab.surface.P2Albedo'> insolation: <class 'climlab.radiation.AnnualMeanInsolation'>- Attributes:
- S0
depthDepth at grid centers (m)
depth_boundsDepth at grid interfaces (m)
diagnosticsDictionary access to all diagnostic variables
inputDictionary access to all input variables
latLatitude of grid centers (degrees North)
lat_boundsLatitude of grid interfaces (degrees North)
levPressure levels at grid centers (hPa or mb)
lev_boundsPressure levels at grid interfaces (hPa or mb)
lonLongitude of grid centers (degrees)
lon_boundsLongitude of grid interfaces (degrees)
timestepThe amount of time over which
step_forward()is integrating in unit seconds.
Methods
add_diagnostic(name[, value])Create a new diagnostic variable called
namefor this process and initialize it with the givenvalue.add_input(name[, value])Create a new input variable called
namefor this process and initialize it with the givenvalue.add_subprocess(name, proc)Adds a single subprocess to this process.
add_subprocesses(procdict)Adds a dictionary of subproceses to this process.
compute()Computes the tendencies for all state variables given current state and specified input.
compute_diagnostics([num_iter])Compute all tendencies and diagnostics, but don't update model state.
declare_diagnostics(diaglist)Add the variable names in
inputlistto the list of diagnostics.declare_input(inputlist)Add the variable names in
inputlistto the list of necessary inputs.diffusive_heat_transport()Compute instantaneous diffusive heat transport in unit \(\textrm{PW}\) on the staggered grid (bounds) through calculating:
global_mean_temperature()Convenience method to compute global mean surface temperature.
inferred_heat_transport()Calculates the inferred heat transport by integrating the TOA energy imbalance from pole to pole.
integrate_converge([crit, verbose])Integrates the model until model states are converging.
integrate_days([days, verbose])Integrates the model forward for a specified number of days.
integrate_years([years, verbose])Integrates the model by a given number of years.
remove_diagnostic(name)Removes a diagnostic from the
process.diagnosticdictionary and also delete the associated process attribute.remove_subprocess(name[, verbose])Removes a single subprocess from this process.
set_state(name, value)Sets the variable
nameto a new statevalue.set_timestep([timestep, num_steps_per_year])Calculates the timestep in unit seconds and calls the setter function of
timestep()step_forward()Updates state variables with computed tendencies.
to_xarray([diagnostics])Convert process variables to
xarray.Datasetformat.
- class climlab.model.ebm.EBM_seasonal(a0=0.33, a2=0.25, ai=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
EBMA class that implements Energy Balance Models with realistic daily insolation.
This class is inherited from the general
EBMclass and uses the insolation subprocessDailyInsolationinstead ofP2Insolationto compute a realisitc distribution of solar radiation on a daily basis.If argument for ice albedo
'ai'is not given, the model will not have an albedo feedback.An instance of
EBM_seasonalis initialized with the following arguments:- Parameters:
a0 (float) – base value for planetary albedo parametrization
StepFunctionAlbedo[default: 0.33]a2 (float) – parabolic value for planetary albedo parametrization
StepFunctionAlbedo[default: 0.25]ai (float) – value for ice albedo paramerization in
StepFunctionAlbedo(optional)
Object attributes
Following object attributes are updated during initialization:
- Variables:
param (dict) – The parameter dictionary is updated with
'a0'and'a2'.subprocess (dict) – suprocess
'insolation'is overwritten byDailyInsolation.
if
'ai'is not given:- Variables:
if
'ai'is given:- Variables:
param (dict) – The parameter dictionary is updated with
'ai'.subprocess (dict) – suprocess
'albedo'is overwritten byStepFunctionAlbedo(which basically has been there before but now is updated with the new albedo parameter values).
- Example:
The annual distribution of solar insolation:
import climlab from climlab.utils import constants as const import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # creating model model = climlab.EBM_seasonal() model.step_forward() solar = model.subprocess['insolation'].insolation # plot fig = plt.figure( figsize=(6,4)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111) season_days = const.days_per_year/4 for season in ['winter','spring','summer','autumn']: ax.plot(model.lat, solar, label=season) model.integrate_days(season_days) ax.set_title('seasonal solar distribution') ax.set_xlabel('latitude') ax.set_xticks([-90,-60,-30,0,30,60,90]) ax.set_ylabel('solar insolation (W/m$^2$)') ax.legend(loc='best') plt.show()
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)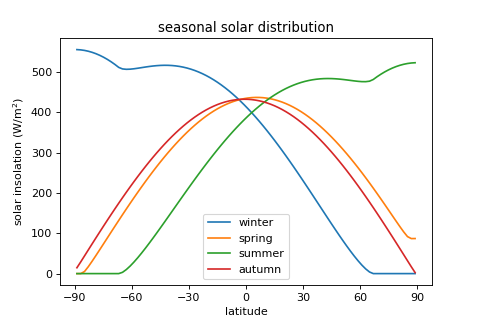
- Attributes:
- S0
depthDepth at grid centers (m)
depth_boundsDepth at grid interfaces (m)
diagnosticsDictionary access to all diagnostic variables
inputDictionary access to all input variables
latLatitude of grid centers (degrees North)
lat_boundsLatitude of grid interfaces (degrees North)
levPressure levels at grid centers (hPa or mb)
lev_boundsPressure levels at grid interfaces (hPa or mb)
lonLongitude of grid centers (degrees)
lon_boundsLongitude of grid interfaces (degrees)
timestepThe amount of time over which
step_forward()is integrating in unit seconds.
Methods
add_diagnostic(name[, value])Create a new diagnostic variable called
namefor this process and initialize it with the givenvalue.add_input(name[, value])Create a new input variable called
namefor this process and initialize it with the givenvalue.add_subprocess(name, proc)Adds a single subprocess to this process.
add_subprocesses(procdict)Adds a dictionary of subproceses to this process.
compute()Computes the tendencies for all state variables given current state and specified input.
compute_diagnostics([num_iter])Compute all tendencies and diagnostics, but don't update model state.
declare_diagnostics(diaglist)Add the variable names in
inputlistto the list of diagnostics.declare_input(inputlist)Add the variable names in
inputlistto the list of necessary inputs.diffusive_heat_transport()Compute instantaneous diffusive heat transport in unit \(\textrm{PW}\) on the staggered grid (bounds) through calculating:
global_mean_temperature()Convenience method to compute global mean surface temperature.
inferred_heat_transport()Calculates the inferred heat transport by integrating the TOA energy imbalance from pole to pole.
integrate_converge([crit, verbose])Integrates the model until model states are converging.
integrate_days([days, verbose])Integrates the model forward for a specified number of days.
integrate_years([years, verbose])Integrates the model by a given number of years.
remove_diagnostic(name)Removes a diagnostic from the
process.diagnosticdictionary and also delete the associated process attribute.remove_subprocess(name[, verbose])Removes a single subprocess from this process.
set_state(name, value)Sets the variable
nameto a new statevalue.set_timestep([timestep, num_steps_per_year])Calculates the timestep in unit seconds and calls the setter function of
timestep()step_forward()Updates state variables with computed tendencies.
to_xarray([diagnostics])Convert process variables to
xarray.Datasetformat.
